Researchers have found how a cell floor protein known as Aplp1 can play a task in spreading materials answerable for Parkinson’s illness from cell-to-cell within the mind.
Promisingly, an FDA-approved most cancers drug that targets one other protein known as Lag3 – which interacts with Aplp1 – blocks the unfold in mice, suggesting a possible remedy could exist already.
In a current paper, a world group of scientists describes how the 2 proteins work collectively to assist dangerous alpha-synuclein protein clumps get into mind cells.
“Now that we all know how Aplp1 and Lag3 work together, now we have a brand new approach of understanding how alpha-synuclein contributes to the illness development of Parkinson’s illness,” neuroscientist Xiaobo Mao from Johns Hopkins College stated in June.
“Our findings additionally recommend that focusing on this interplay with medicine may considerably gradual the development of Parkinson’s illness and different neurodegenerative ailments.”
Greater than 8.5 million individuals globally have Parkinson’s, the second commonest neurodegenerative illness after Alzheimer’s.
As a progressive motion dysfunction, it is normally solely recognized when signs present, which embrace tremors, stiffness, steadiness issues, speech difficulties, disturbed sleep patterns, and psychological well being points. At present incurable, the illness means sufferers could finally battle to stroll or communicate.
Parkinson’s signs primarily end result from the dying or impairment of dopamine-producing neurons within the mind’s substantia nigra, a area concerned in fantastic motor management. That is considered attributable to Lewy our bodies, that are irregular clumps of protein principally consisting of misfolded alpha-synuclein that journey between neurons.
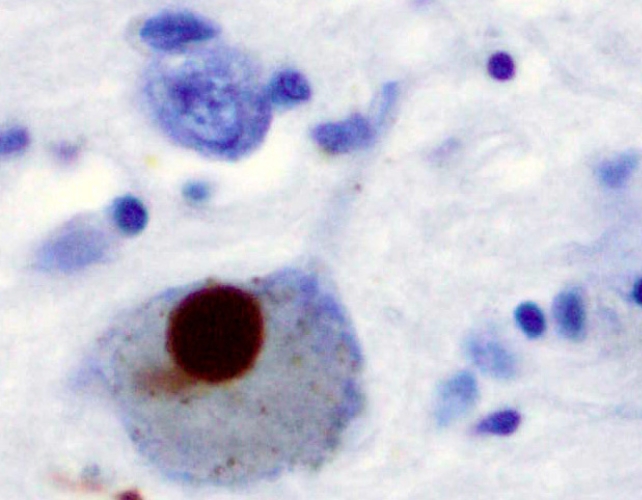
Alpha-synuclein usually maintains useful communication between neurons, however issues come up when it turns into misfolded and insoluble. That stated, figuring out whether or not that is a reason behind Parkinson’s or a symptom is troublesome.
Previous research on mice discovered Lag3 binds to alpha-synuclein proteins and spreads Parkinson’s illness pathology in neurons. Whereas deleting Lag3 considerably impedes this course of, it doesn’t utterly forestall it, indicating one other protein was additionally implicated in neurons taking in misfolded alpha-synuclein.
“Our work beforehand demonstrated that Lag3 wasn’t the one cell floor protein that helped neurons take in alpha-synuclein, so we turned to Aplp1 in our most up-to-date experiments,” stated Johns Hopkins neuroscientist Valina Dawson.
The scientists performed exams with genetically modified mice that have been lacking both Aplp1 or Lag3, or each. They discovered Aplp1 and Lag3 can every independently assist mind cells take in dangerous alpha-synuclein, however collectively they considerably improve the uptake.
When mice have been lacking each Aplp1 and Lag3, 90 % much less of the dangerous alpha-synuclein entered wholesome mind cells, that means a better quantity of the dangerous protein clumps was blocked with each proteins lacking in contrast with a deletion of only one.
The researchers gave regular mice the drug nivolumab/relatlimab, a melanoma treatment that accommodates a Lag3 antibody, and located that it additionally stopped Aplp1 and Lag3 from interacting, once more nearly utterly blocking the formation of disease-causing alpha-synuclein clumps in neurons.
“The anti-Lag3 antibody was profitable in stopping additional unfold of alpha-synuclein seeds within the mouse fashions and exhibited higher efficacy than Lag3-depletion due to Aplp1’s shut affiliation with Lag3,” stated Ted Dawson, a neuroscientist at Johns Hopkins College.
The following step can be to check the Lag3 antibody on mouse fashions of Parkinson’s illness and Alzheimer’s – the place analysis has pointed to Lag3 as a goal too.
The analysis has been printed in Nature Communications.
An earlier model of this text was printed in June 2024.



